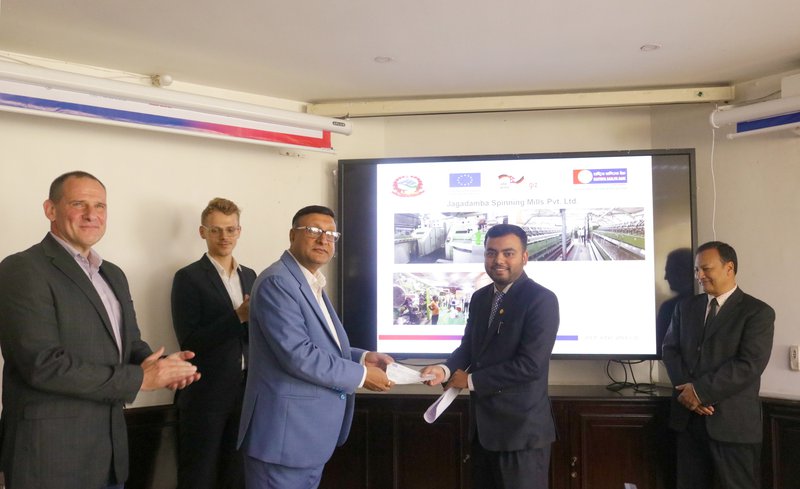


Caption: Devendra Raman Khanal, Chief Executive Officer of RBBL of Rastriya Banijya Bank is distributing grant in presence of (From left) Dr. Frank Fecher, Project Manager of the REEEP GREEN, Jan Dirksen, Deputy Head of Cooperation at the Embassy of the Federal Republic of Germany and Ranzan Prakash Shrestha, Senior Program Manager of the European Delegation.
As Nepal continues its uphill journey toward sustainable development, few international development agencies have remained as consistently impactful as the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ). Over the past 50 years, GIZ’s partnership with Nepal has grown into one of the most effective examples of long-term technical cooperation in the renewable energy sector.
From pioneering micro-hydro electrification in remote villages to advising on national energy strategies, GIZ has not only facilitated energy access but also shaped the very frameworks that define Nepal’s energy future. Its contribution has transcended traditional aid, focusing instead on system-level transformation, capacity building, and policy reform—pillars necessary for a resilient green economy.
“GIZ technical support to renewable energy sector is immense. Alternative Energy Promotion Center (AEPC) has been implementing several projects to largely benefits rural population,” said Nawaraj Dhakal, Executive Director of AEPC. GIZ has backed Nepal’s energy sector providing technical support to promote and develop renewable energy.”
Renewable Energy as Climate Action (REEEP-GREEN)
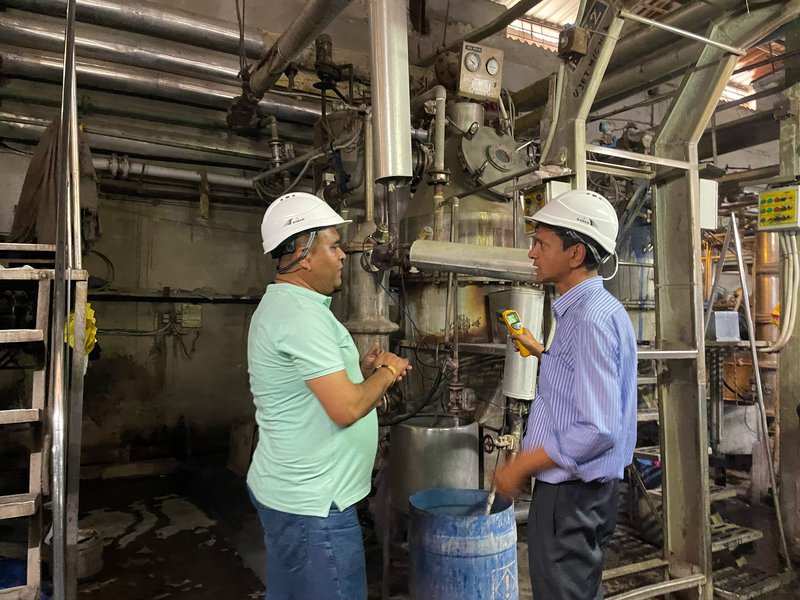

Caption: REEEP-GREEN supports industries in improving energy efficiency and competitiveness.
Co-funded by the European Union (EU) and the Federal Republic of Germany, and implemented by GIZ in close collaboration with the Ministry of Energy, Water Resources and Irrigation, as well as the Alternative Energy Promotion Center (AEPC), the Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency Program – Green Recovery and Empowerment with Energy in Nepal (REEEP-GREEN) has been bringing significant changes to Nepal's energy sector.
GIZ’s evolving portfolio in Nepal has increasingly aligned with global climate goals. Programs such as REEEP-GREEN and RERA reflect this shift, focusing not just on energy supply but on emission reduction, low-carbon technologies, and climate-smart planning.
The REEEP-GREEN program, launched in 2021 and co-funded by the EU and Germany, is a cornerstone of this climate-focused strategy. In just one year (2022), it helped Nepal save 165,000+ MWh of energy and cut 36,870 tons of CO2 equivalents. Moreover, it promoted local ownership by empowering 100 municipalities to develop Renewable Energy Policies and Sub-Committees—bringing climate action down to the local level.
Similarly, RERA (2016–2022) encouraged 16 rural municipalities to incorporate IT-based energy planning and allocated NPR 1 billion for renewable energy, showcasing the success of data-driven local governance.
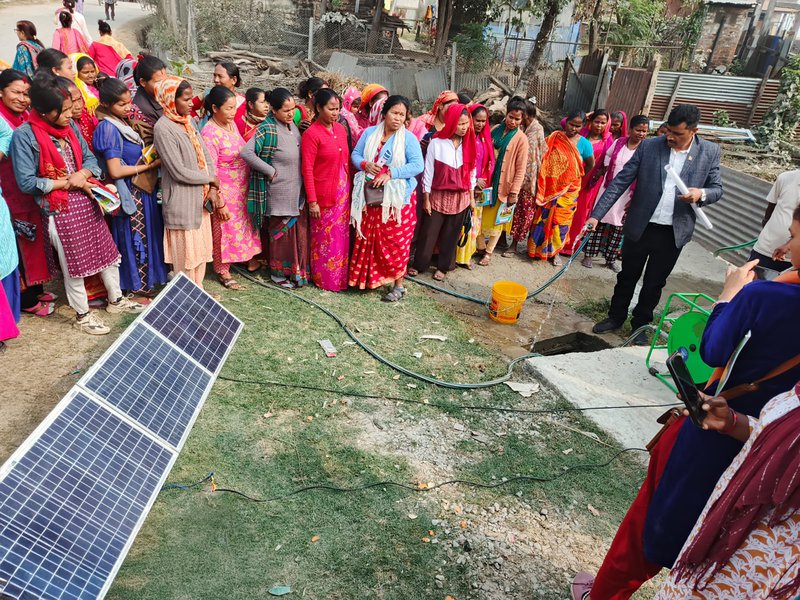

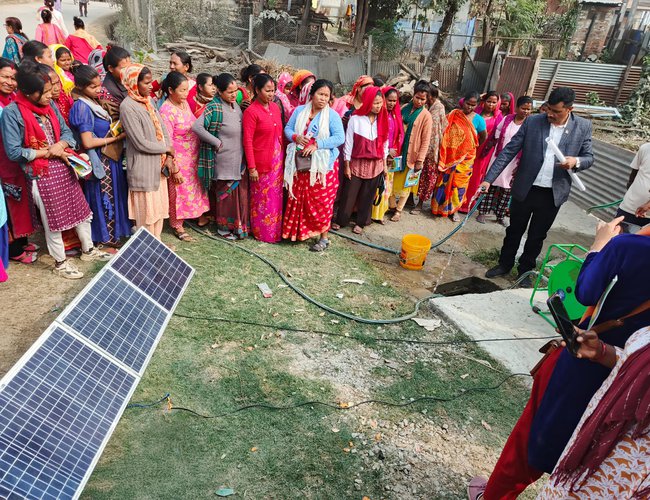
Caption: More than 55,000 people have received easy access to affordable renewable energy technologies in Nepal via cooperatives through REEEP-GREEN support.
The Evolution of GIZ’s Role
In the early decades of partnership, GIZ’s focus was primarily on expanding rural electrification through small-scale renewable technologies such as micro-hydropower and improved cook stoves. Projects like the Small Hydropower Promotion Project (2000–2009)* laid critical infrastructure for decentralized energy production. By enabling over 100 small hydro plants and supporting the establishment of the Small Hydropower Developers Association – Nepal (SHDAN), GIZ helped electrify tens of thousands of households in off-grid areas.
But over time, GIZ’s approach matured from infrastructure delivery to institutional development. The agency played an instrumental role in developing a Rural Energy Policy, a milestone document that guided national electrification efforts in the 2000s. This shift—from hardware to governance—marked a turning point in Nepal’s energy transition.
Institutionalizing Energy Efficiency and Strategic Planning
One of GIZ’s most enduring contributions lies in its support for strategic energy planning. Through the Nepal Energy Efficiency Programme (NEEP I & II) from 2010 to 2021, GIZ facilitated the formulation of the Biomass Energy Strategy (BEST) and the Energy Efficiency Strategy (EEST)—documents that remain cornerstones in Nepal’s energy policy landscape.
Crucially, GIZ didn’t stop at high-level planning. It operationalized these strategies by training over 1,000 leaders in energy efficiency, supporting 100 municipalities in developing five-year energy development plans, and helping industries save more than 220,000 MWh of energy annually through energy audits.
This approach exemplifies GIZ’s model: integrate policy with practice, and ensure that reform reaches the last mile—from the ministry to the municipality.
Energizing Development
Since 2009, the Energizing Development Nepal (ENDEV) initiative has become a flagship success story in development cooperation. ENDEV has connected over 350,000 people to electricity and enabled 4,200 businesses and 1,700 public institutions—like schools and health posts—to operate more effectively.

Women empowerment through power
Perhaps more importantly, it addressed energy poverty not just through electricity but also through clean cooking technologies. The distribution of electric cooktops and improved cook stoves to 160,000+ people demonstrated how access to energy, when coupled with behavior change and gender sensitivity, can uplift rural women and improve health outcomes.
Supporting Nepal’s Green Transport Ambitions
GIZ is also breaking ground in the transport sector. The *Sustainable Electric Transport for Nepal (SET4NPL)* initiative (2023–2028) targets the deployment of 3,500 electric micro and mini-buses, offering a practical path toward cleaner public mobility. By supporting the Government in achieving its Second Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), this initiative exemplifies how GIZ is aligning local development goals with international climate commitments.
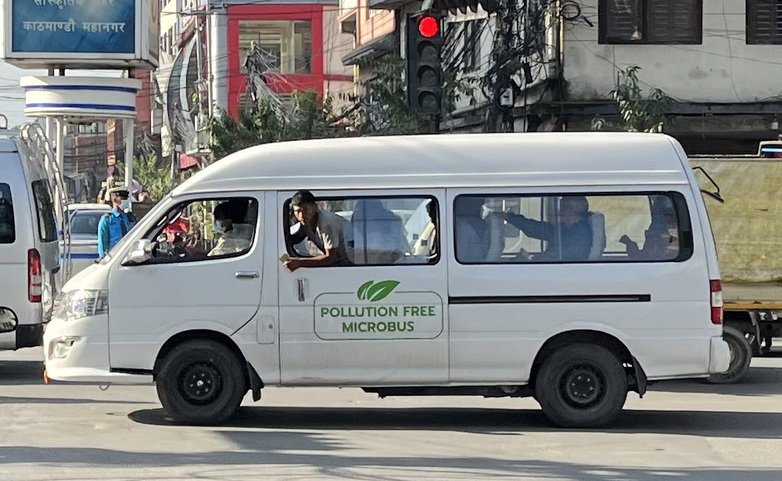

Caption SET4NPL project plans to bring 3,500+ Electric Micro and Mini-Buses (EMBs) to the public transport fleet through business and financing models. REEEP-GREEN has provided technical and financial support to private sector for installation of charging stations in 10 different locations across the country.
A Model of Long-Term Development Partnership
Fifty years of GIZ’s partnership in Nepal exemplify the power of consistency, trust, and adaptability in development cooperation. What began as a focus on rural electrification has evolved into a robust platform for policy reform, technological innovation, and climate resilience.
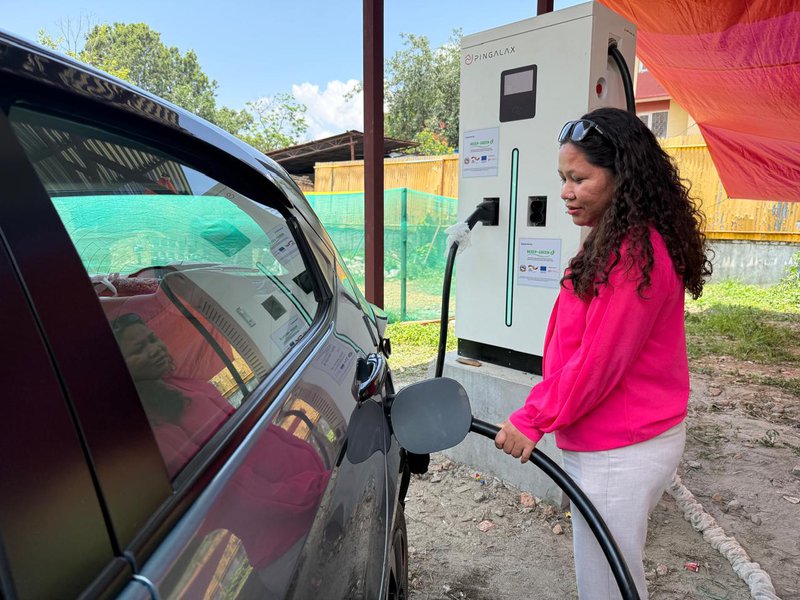
Support to Electric Charging stations to boost electric vehicles
Unlike many short-term interventions, GIZ’s work in Nepal shows that sustainable development is a cumulative process—built brick by brick through local capacity, national vision, and international solidarity. As Nepal navigates the twin challenges of energy security and climate change, GIZ remains not just a partner but a catalyst for transformation.
GIZ's ongoing support in the renewable energy sector and energy efficiency has played a crucial role in helping Nepal achieve energy security in the long term.
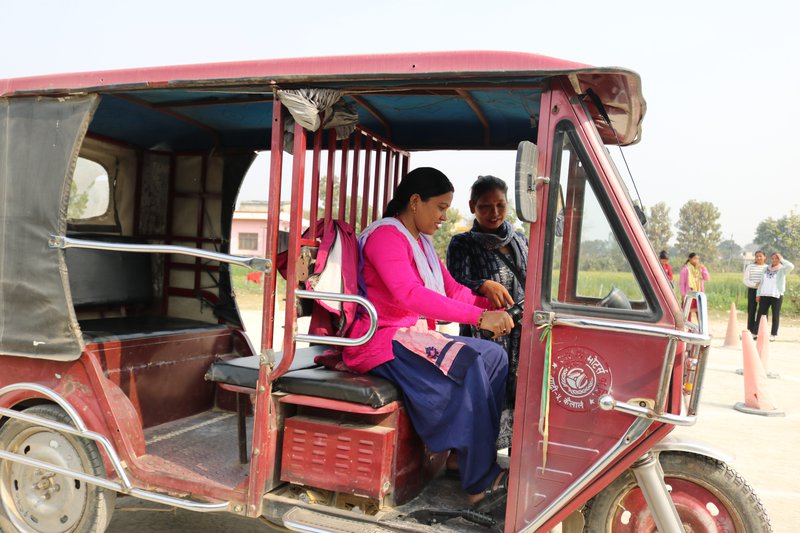

Caption: Electric rickshaws: Affordable loan facilities for electric rickshaws drivers
Photos courtesy: REEEP -GREEN Project
- Welfare Fund Contributes to Social Development: Prime Minister Oli
- Jul 31, 2025
- Bhotekoshi Flash Flood: Road Erosion, Damage to Hydropower
- Jul 31, 2025
- Weather Forecast: Generally Cloudy Across The Country Possibility Of Rain In Lumbini And Sudurpaschim Provinces
- Jul 31, 2025
- Nepal Investment Mega Bank Limited Launches 'Instant EMI' Facility For the First Time in Nepal
- Jul 30, 2025
- Prime Minister Inaugurates Rani Jamara Kulariya Irrigation Three Years After Completion
- Jul 30, 2025















