
Meteorologist Sudarshan Humagai of the Department of Water and Meteorology in the Forum on Monsoon Rainfall and Temperature Assessment said that there will be more than average rainfall during the monsoon period from June 1 to September 30. Looking at it in probability, there is a 35 to 55 percent chance of more than normal rainfall in most parts of the country.
National Monsoon Forum, 2081, in a public program organized today about the upcoming monsoon situation, Meteorologist Sudarshan Humagai in the department informed that there is a possibility of 35.4 percent to 55.4 percent more rain than Sardar in most places.
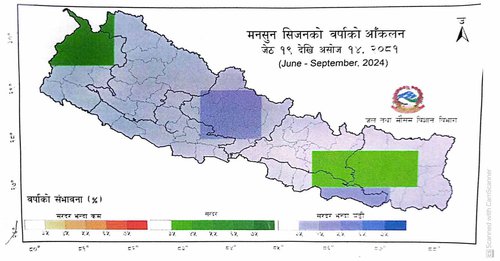
The probability of rainfall exceeding Sardar is 35.4 percent to 65.5 percent in the north-western part of Sudurpaschim province, the south-eastern part of Bagmati province, the central part of Madhes province and the central and central-western part of Koshi province.
Also, the department said that there is a 35 to 45 percent chance of rain in the western part of Karnali province, the central part of Gandaki province and the north-eastern part of Koshi province.
Also, the minimum temperature in most places of the country has a probability of 35 to 65.4 percent.
According to meteorologist Humagai, there is a 35 to 45 percent chance of heavy rain in the north-western part of Sudurpaschim province, south-eastern part of Bagmati province, central part of Madhesh province and central and central-western part of Koshi province.
Both the maximum and minimum temperatures are seen to be above average during this period. 80 percent of the annual rainfall falls during the monsoon period.
INDIA METEOROLOGICAL DEPARTMENT Long Range Forecast
The 2024 southwest monsoon seasonal (June to September) rainfall over the country as a whole is most likely to be above normal (>104% of the Long Period Average (LPA)).
Quantitatively, the seasonal rainfall over the country as a whole is likely to be 106% of LPA with a model error of ± 5%. The LPA of the season rainfall over the country as a whole for the period 1971-2020 is 87 cm. b) Currently, moderate El Niño conditions are prevailing over the equatorial Pacific region.
The latest Monsoon Mission Climate Forecast System (MMCFS) as well as other climate model forecasts indicate that the El Niño condition is likely to weaken further to neutral El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) conditions during early part of the monsoon season and La Niña conditions are likely to develop during second half of monsoon season.
c) At present, neutral Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) conditions are prevailing over the Indian Ocean and the latest Climate model forecasts indicate that the positive IOD conditions are likely to develop during the later part of the southwest monsoon season.
d) The northern hemisphere snow cover extent during the last three months (January to March, 2024) was below normal. Winter and spring snow cover extent over Northern Hemisphere as well as Eurasia has a generally inverse relationship with the subsequent Indian summer monsoon rainfall. IMD will issue the updated forecasts for monsoon season rainfall in the last week of May, 2024.
2 1. Background Since 2003, India Meteorological Department (IMD) has been issuing the operational long-range forecast (LRF) for the southwest monsoon seasonal (JuneSeptember) rainfall averaged over the country as a whole in two stages. The first stage forecast is issued in April and the second stage updated forecast is issued by the end of May. In 2021, IMD has implemented a new strategy for issuing monthly and seasonal operational forecasts for the southwest monsoon rainfall over the country by modifying the existing two stage forecasting strategy.
The new strategy uses both dynamical and statistical forecasting system. Multi-Model Ensemble (MME) forecasting system based on coupled global climate models (CGCMs) from different global climate prediction centres, including IMD’s Monsoon Mission Climate Forecast System (MMCFS) are used in dynamical forecast system.
As per the new LRF strategy, the first stage forecast issued in middle of April consist of quantitative and probabilistic forecasts for the country as a whole and the spatial distribution of probabilistic forecasts for the tercile categories (above normal, normal, and below normal) of the seasonal rainfall (June-September) over the country.
The second stage forecast issued around end of May consists of update for the seasonal rainfall forecast issued in April along with the probabilistic forecasts for the seasonal rainfall over the four homogenous regions of India (northwest India, central India, south Peninsula and northeast India) and monsoon core zone (MCZ). In addition, quantitative and probabilistic forecasts for the country as a whole and the spatial distribution of probabilistic forecasts of rainfall (above normal, normal, and below normal) over the country during June are also issued during the second stage forecast.
In continuation to the above forecasts, monthly rainfall forecast is issued around end of June, July and August respectively for the subsequent one month. In addition, quantitative and probabilistic forecasts for the country as a whole, and the spatial distribution of probabilistic forecasts of rainfall for the second half (August – September) of the season is issued around end of July along with the forecast for August. 3 2. Forecast for the monsoon Season (June–September) rainfall over the country as a whole.
The forecast based on both dynamical and statistical models suggests that quantitatively, the monsoon seasonal rainfall during June to September is likely to be 106% of the Long Period Average (LPA) with a model error of ± 5%. The LPA of the season rainfall during June to September over the country as a whole based on the data of 1971-2020 is 87 cm. The five category probability forecasts for the Seasonal (June to September) rainfall over the country as a whole are given below. It suggests that there is high probability (61%) of southwest monsoon seasonal rainfall to be above normal (>104% of LPA).
The MME forecast for the 2024 southwest monsoon season rainfall was prepared based on the April initial conditions and using a group of coupled climate models which have highest prediction skill over the Indian monsoon region.
The spatial distribution of probabilistic forecasts for tercile categories (above normal, normal and below normal) for the seasonal rainfall (June to September) is shown in Fig.1. The spatial distribution suggests that above normal seasonal rainfall is very likely over most parts of the country except some areas over Northwest, East and Northeast India, where below normal rainfall is very likely.
The model has no clear signal over the white shaded areas of the country as presented in Fig.1. Category Rainfall Range (% of LPA) Forecast Probability (%) Climatological Probability (%) Deficient < 90 2 16 Below Normal 90 - 96 8 17 Normal 96 -104 29 33 Above Normal 104 -110 31 16 Excess > 110 30 17 4 3. Sea Surface Temperature (SST) Conditions in the equatorial Pacific & Indian Oceans Currently, moderate El Niño conditions are prevailing over the equatorial Pacific region. The latest MMCFS as well as other climate model forecasts indicate that El Niño conditions are likely to weaken further to neutral El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) condition in the early part of the monsoon season and La Niña conditions are likely to develop during second half of monsoon season.
At present, neutral Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) conditions are prevailing over the Indian Ocean and the latest climate model forecasts indicate that the positive IOD conditions are likely to develop during the later part of the southwest monsoon season.
As sea surface temperature (SST) conditions over the Pacific and the Indian Oceans are known to have a strong influence on the Indian monsoon, IMD is carefully monitoring the evolution of sea surface conditions over these Ocean basins. 4. Snow Cover over the Northern Hemisphere Winter and spring snow cover extent over Northern Hemisphere as well as Eurasia has a generally inverse relationship with the subsequent Indian summer monsoon rainfall.
The northern hemisphere snow cover areas during January to March 2024 were observed to be below normal. The expected La Nina, positive IOD and below normal snow cover over northern hemisphere would be favourable for rainfall during southwest monsoon season, 2024. 5 Probablistic rainfall forecast for monsoon season (June –
- Snow Cover over the Northern Hemisphere Winter and spring snow cover extent over Northern Hemisphere as well as Eurasia has a generally inverse relationship with the subsequent Indian summer monsoon rainfall. The northern hemisphere snow cover areas during January to March 2024 were observed to be below normal. The expected La Nina, positive IOD and below normal snow cover over northern hemisphere would be favourable for rainfall during southwest monsoon season, 2024.
- India’s External Affairs Ministry’s Senior Officials Says Indo-Nepal relations are ever expanding
- Jul 05, 2025
- Bhutan Government Unveils Three Pronged Strategies To Tackle Skilled Migration Crisis
- Jul 05, 2025
- Weather Forecast: Generally Cloudy Across The Country With Heavy Rain At One Or Two Places Bagmati And Koshi Provinces
- Jul 05, 2025
- FNCCI President Dhakal Urges British Companies to Invest in Nepal
- Jul 04, 2025
- Nepal Is Expected To See 60,000 People Infected with Dengue This Year
- Jul 04, 2025















